- Different data storage locations:
Cookie data is stored in the client’s browser, while session data is stored on the server.
- Different security levels:
Cookies are not very secure. Others can analyze the cookies stored locally and carry out cookie spoofing. For security reasons, sessions should be used.
- Different performance usage levels:
Sessions are stored on the server for a certain period of time. When the number of visits increases, it will take up more server performance. To reduce server performance pressure, cookies should be used.
- Different data storage sizes:
A single cookie can store no more than 4K of data, and many browsers limit a site to a maximum of 20 cookies. However, sessions are stored on the server side, and there is no such restriction from the browser.
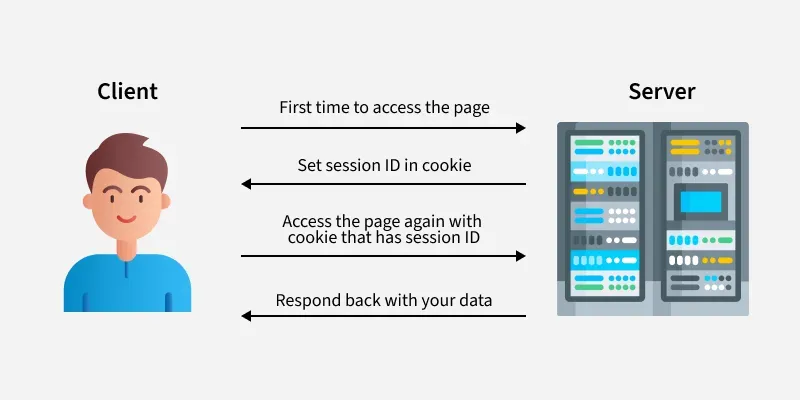
Introduction to cookie
A cookie is actually a small piece of text information. When a client requests a server, if the server needs to record the user’s status, it will issue a cookie to the client’s browser using a response. The client’s browser will save the cookie. When the browser requests the website again, it will submit the requested URL along with the cookie to the server. The server checks the cookie to identify the user’s status. The server can also modify the content of the cookie as needed.
Understanding: A cookie is a session pass. It is stored in the browser.
A cookie can be set with a retention time and will be kept throughout the validity period; while a session is at the session level. When the session ends, the session is also cleared accordingly. This is also the reason why it is necessary to clear the browser cache.
Introduction to session
Sessions are stored on the server. When a client browser accesses the server, the server records the client information in some form on the server. This is a session. When the client browser visits again, it only needs to find the client’s status from the session.
Understanding: A session is the storage of changes in the current session. It is stored on the server.
Session: For a login request (request headers), the server returns a session (response headers), and the session may change with each request.